Signal Integrity
Outer Loop Equalization for PCIe Cross-Lane Transceiver Optimization
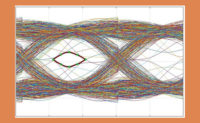
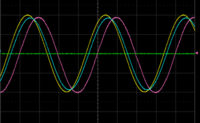
PCIe Gen4 Standards Margin-Assisted Outer-Layer Equalization for Cross-Lane Optimization in a 16GT/s PCIe Link
Read More
New Digital Signal Controller (DSC) Accelerates DSP Performance for Time-Critical Control Applications
dsPIC33CK is Microchip’s highest performance single-core DSC in an ultra-small package
Read More